If you are pursuing a masters in teaching, you may want to explore combined masters and teaching credential programs.

A combined credential and master’s program can allow you to work on obtaining your master’s degree and your teaching credentials at the same time. This can potentially cut down on the cost and time spent on your education.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Attending a combined program can help you develop the skills and experience you need to attain state licensure and pursue a career in education upon graduation.
Combined Masters and Teaching Credential Programs

If you want to begin or continue your education as a teacher, a combined master’s & credential program can be beneficial.
These programs are often designed for students who want to pursue a Master of Education (M.Ed.) or a Master of Arts in Teaching (M.A.T.) along with teaching credentials. Topics studied in MEd and MAT programs are similar, but the choice of which one to choose depends on your career goals and interests.
| M.Ed. | M.A.T |
|
|
Joint master’s degree and teaching credential programs are typically full-time, 16 month programs completed over four semesters. They are often offered on campus, online, or in a hybrid format at many colleges and universities.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
A combined credential and master’s program is designed for students to earn both their master’s degree and their teaching credentials simultaneously. Teacher credentialing programs prepare students for state licensure. To teach in a public or private school, state licensure is nearly always required.
All states have different licensing requirements, so it’s beneficial to check with your state’s education department before enrolling in a combined master’s and credential program.
Teaching Careers & Salaries
With a master’s in teaching, you may have work opportunities in a variety of industries. Teaching jobs are often the most common, but there are many other career paths you can pursue with a masters as well.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, elementary and secondary schools hire the majority of all teachers with masters degrees.
Educational support services, religious organizations, colleges, universities, and state government jobs also hire a great number of graduate-level teachers. Principals holding a master’s degree generally make the highest salaries on average.
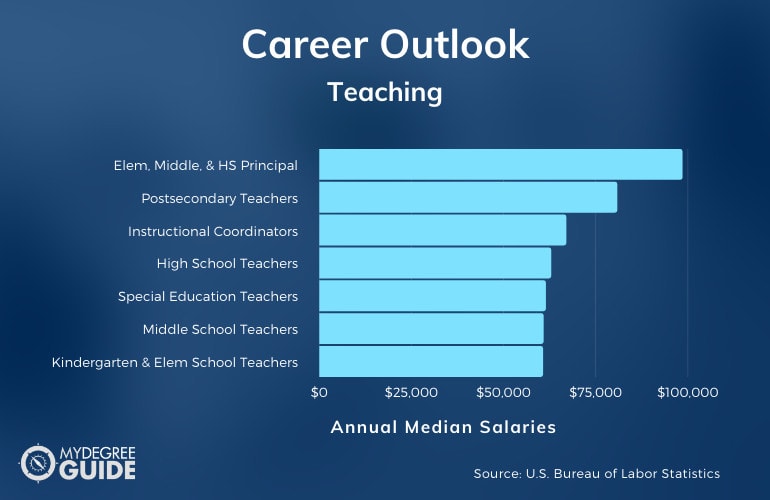
Here are just some of the jobs that can be pursued with a master’s in teaching, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
| Careers | Annual Median Salaries |
| Elementary, Middle School, and High School Principals | $98,490 |
| Postsecondary Teachers | $80,790 |
| Instructional Coordinators | $66,970 |
| High School Teachers | $62,870 |
| Special Education Teachers | $61,420 |
| Middle School Teachers | $60,810 |
| Kindergarten and Elementary School Teachers | $60,660 |
| Career and Technical Education Teachers | $59,140 |
| Adult Basic and Secondary Education and ESL Teachers | $55,350 |
| Preschool Teachers | $31,930 |
Some of the jobs listed above may require additional licensure, degrees, or specializations to obtain. For instance, most universities require a doctorate degree for entry-level postsecondary teaching positions. Many community colleges, though, hire professors with masters degrees.
There are also non-teaching careers, such as educational consultant or curriculum developer, where a master’s degree is often required.
Master’s in Education & Teaching Curriculum

Your classes will vary depending on the university you attend, but master’s programs in education or teaching typically have courses like the following:
- Curriculum Design and Assessment: This course can help you learn how to design a curriculum, from course outlines to content mapping and learning objectives.
- Coping with Stress in Today’s Classroom: This course addresses a variety of issues in children’s lives that impact their education. It also addresses the role of the teacher in providing support.
- School, Community, and Diverse Family Structures: This course can help you develop the skills needed to work with families from culturally and socioeconomically diverse backgrounds.
- Brian-Based Teaching and Learning: This course is designed to provide teachers with the latest research in brain-based learning and instructional theory.
- Developing Character and Ethics: This course provides instruction for how to weave ethical themes and character development into today’s schools.
- Curriculum Theory and History: This class covers the history and design of various educational activities.
- Principles of Teaching and Learning: This course is an examination of the relationships between teaching, learning, and assessment.
- Instructional Models in the Education of Gifted Children: This class can help you learn how to differentiate between different curriculums to meet the needs of gifted children.
- Gender, Difference, and Curriculum: This course is an introduction to school curriculums, policies, and practices as they pertain to gender.
- Critical Perspectives in Elementary Education: This class examines the experiences, practices, and purposes of elementary teachers in the U.S. today.
This is just a sampling of the courses you may have in your master’s program. The courses you study as a master’s student will depend on the requirements of your program.
Admissions Requirements

The admissions requirements for combined master’s and teaching credential programs are similar to the admission requirements for all master’s programs.
Typically, the following items are required for a combined master’s and teaching credential program:
- GRE or GMAT scores (only some schools require them)
- Bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution
- Minimum 3.0 GPA
- Letters of recommendation
- Specified prerequisites and experience
Requirements and policies will vary based on the institution, so it is helpful to check a school’s admission requirements before applying.
Accreditation

It’s important to ensure the school you are attending is regionally accredited. Accreditation certifies that the school has met the highest levels of academic quality set forth. Regionally accredited schools have participated in a rigorous screening process to ensure all standards have been met.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Attending a non-accredited school may impact your financial aid and employment opportunities. Many forms of financial aid are only awarded to accredited programs, and many employers only recognize degrees from accredited programs. Online education degree programs are held to the same standards as all universities and programs. To see if your program is accredited, you can visit the U.S. Department of Education.
Teaching Licensure and Certifications

Teaching certification or licensing is the process that a teacher needs to go through in order to be able to teach in a particular state. Each state has its own name and requirements for this process.
If you plan on teaching, it is beneficial to research the licensure requirements of your state before enrolling in a program. It’s also helpful to have an idea of what you want to teach. Licensing requirements vary depending on grade level and subject matter.
What degree do you need to be a teacher? A bachelor’s degree is required in every state for licensure. In addition, most states require a combination of certifications, field experience, and continuing education requirements.
Financial Aid and Scholarships

If you qualify, you may be able to receive financial aid and scholarships for your combined master’s degree and teaching program. Federal and state governments award financial aid to graduate students based on need.
To see if you qualify, you can fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). Depending on where and what you plan to teach, you may also qualify for the Teacher Education Assistance for College and Higher Education (TEACH) Grant.
This grant is given to students who agree to teach in a “high needs” area for 4 years. This might be a certain school, such as a public high school in an impoverished area, or a certain subject area, such as mathematics or bilingual education.
You can check with your program to see if you can qualify for the TEACH Grant. There may also be scholarship opportunities available. You may find aid from nonprofit organizations, your place of employment, or your program’s education department.
What Is a Teaching Credential Program?

A teaching credential program is the certification process you need to go through in order to obtain a state-issued license to teach in a public school.
Most licensing programs require you to pass a test in order to receive the license. A teaching credential program is designed to help prepare you to pass this exam. Depending on what you plan to teach, you can enroll in a multiple subject, single subject, preschool, bilingual, or special education teaching credential program.
Is a Teaching Credential a Masters Degree?
No, a teaching credential is not the same as a master’s degree. A master’s degree declares that you have mastered the knowledge within a university’s program area.
A teaching credential is the licensure process needed in order to teach within a given state. Each state has its own credentialing process. In order to teach in a public school, you will need your teaching licensure in addition to a bachelors or masters degree.
Can You Get a Masters in Teaching without a Bachelor’s in Teaching?

Yes, you can receive a masters in teaching without holding a bachelors degree in teaching.
A bachelors degree is typically required to enroll in a masters in teaching program, but it does not necessarily need to be a bachelors degree in teaching or education. Many schools allow you to enroll in a combined masters and teaching credential program as long as you hold a bachelor’s degree in any program.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
There are alternative routes that make teaching possible for those who have a bachelor’s degree in an alternative discipline. Before enrolling, you can check with your state’s education department and the program you are applying to for additional requirements.
What Masters Degree Should a Teacher Get?

The master’s degree you should pursue depends on what bachelor’s degree you hold and your goals as a teacher.
There are quite a few programs to choose from depending on the area you intend on specializing in:
- Master of Education
- Master of Arts in Teaching
- Master of Science in Education
- Master’s in English Education
- Master’s in Mathematics Education
- Master’s in Special Education
The Master of Arts in Teaching is beneficial for students who do not have a bachelor’s in education. It is a practical program designed for people who want to teach in the classroom.
The Master of Education is designed for students who intend to work as principals, superintendents, researchers, school counselors, or other academic leadership roles.
What Can You Do with a Master’s Degree with Teaching Credential?

There are many avenues you may pursue with a master’s degree in teaching. You may, of course, continue teaching in both public and private schools. A master’s degree can also help open the door to positions in higher education settings.
You may pursue work in administration and leadership roles as well. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, most principals and superintendents hold master’s degrees. Some graduates even look for work in a non-teaching position, such as educational consultant, corporate trainer, or curriculum developer.
What’s the Difference between Single Subject Credentials vs. Multiple Subjects Teaching Credentials?
Choosing between single subject teaching credentials and multiple subject teaching credentials depends on which subjects and levels you want to teach.
| Single Subject Teaching Credentials | Multiple Subject Teaching Credentials |
|
|
This is just a general idea of the differences between the two. Some high school, preschool, and adult education teachers also pursue multiple subject teaching credentials.
What’s the Difference between a MAT vs. MEd?

A Master of Arts in Teaching (MAT) and a Master of Education (MEd) are two distinct degree paths.
- Master of Arts in Teaching: Students who pursue a MAT typically plan on remaining in the classroom.
- Master of Education: An MEd is geared more towards moving beyond the classroom and into the educational system itself.
MAT students generally desire expert knowledge and specialized skills, looking for a more hands-on, practical approach to working directly with students. The MAT is also beneficial for those interested in teaching but who have a bachelor’s degree in another discipline.
MEd graduates, on the other hand, often work with policies and procedures within educational systems. They may also take on leadership roles.
Is It Worth Getting a Masters in Teaching and Teaching Credential at the Same Time?

Yes, getting a masters in teaching and a teaching credential at the same time is worth it for many students.
A teaching credential is needed to teach, so it can be strategic to pursue both at the same time. Plus, pursuing both simultaneously may cut down on the cost of your education and the time spent enrolled within the program.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the annual median wages are higher for those who hold a master’s degree over a bachelor’s degree in nearly every teaching position. In addition, the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 5% job growth for education, training, and library occupations.
Universities Offering Combined Masters and Teaching Credentials Degree Programs
Methodology: The following school list is in alphabetical order. To be included, a college or university must be regionally accredited and offer degree programs online, on campus, or in a hybrid format.

Ball State University offers a Master’s in Secondary Education degree program that offers a concentration track called the Dual Credit Teaching Credential. This concentration allows students to choose 18 credit hours in a content area, such as Math, English, or Technology. Those interested in the program may apply online.
Ball State is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission.

California University—Fullerton offers a program that allows students to pursue a Multiple Subject Credential and a Master’s in Education.
The program can typically be completed in 16 months and allows students to take courses online or in a hybrid format. The program only begins during the fall semester and requires students to have a GPA of 3.0 or higher.
California State University – Fullerton is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges Senior College and University Commission.

Colorado State University offers an online program named TEACHERREADY. The program allows students to pursue a master’s degree as they receive teaching credentials for grades K through 12. The program requires 36 semester hours. Applicants must have a bachelor’s degree with a GPA of 2.5.
Colorado State is accredited by The Higher Learning Commission, a Commission of the North Central Association of Schools and Colleges.

Dominican University of California offers a Master of Science in Education and Teacher Credentials program.
The program requires students to complete a minimum of 48 units that are offered through a hybrid format. Applicants must have a GPA of 3.0 and 2 letters of recommendation. Applicants may also be required to complete a personal interview.
The Dominican University of California is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges.

Drexel University offers a program that allows students to pursue a Master of Science in Teaching along with dual certification in Secondary and Special Education.
The program requires 48 credit hours and a 12 week student teaching experience. Applicants must have a GPA of 3.0, 2 professional letters of recommendation, a personal essay, and official transcripts.
Drexel University is accredited by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education.

National University offers a Master of Education in Inspired Teaching and Learning with the option to receive teaching credentials. Each course is 4 weeks long and takes place on campus. Applicants must have a GPA of 2.0 or higher to be eligible for the degree.
National University is accredited by the WASC Senior College and University Commission.

The University of California—Davis offers a Master of Arts in Education program that allows students to pursue their teaching credentials at the same time. Students can select teaching credentials from 6 subjects, including Agriculture and Science. Applicants must have a bachelor’s degree with a minimum GPA of 3.0.
UC Davis is accredited by the WASC Senior College and University Commission.

The University of Redlands offers a Master of Arts in Education, Learning, and Teaching. The program offers 3 pathways, including an Educational Specialist Teaching Credential. The program requires students to complete 39 units to graduate. Applicants must have a GPA of 2.75 or higher, official transcripts, and 2 letters of recommendation.
The University of Redlands is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges.

The University of San Diego offers a Master’s in Education that also enables students to obtain teaching credentials.
The program offers a number of credential tracks, including dual credential tracks that allow students to obtain credentials for 2 separate teaching fields. Applicants must submit a resume, official transcripts, 2 letters of recommendation, and a statement of purpose.
The University of San Diego is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges-Senior College and University Commission.

The University of San Francisco offers a dual degree in Teacher Preparation. This program allows students to obtain a bachelor’s degree in a major of their choice, a Master of Arts in Teaching, and teaching credentials.
The teaching credentials may be in multiple subjects for elementary schools or in a single subject for middle and high schools. Applicants must submit AP test scores and 2 essays.
The university also offers an online masters in educational technology for students interested in this specialization.
The University of San Francisco is accredited by the Western Association of Schools and Colleges Senior College and University Commission.
Getting Your Masters in Teaching Online

If you plan on getting your masters in teaching, it can be beneficial to enroll in a combined masters and teaching credential program. All states require a teaching credential to teach in public schools. Most accredited private schools require teaching credentials as well. A number of universities offer online post baccalaureate teacher certification, but these programs do not lead to a masters degree.
By attending a combined online teaching degree program, you can work on completing your teaching credential simultaneously with your masters degree. This way, you can prepare to take your state licensure exam right after graduation. Some combined program graduates continue on and earn an online PhD in Teaching before beginning to work.
If a masters in teaching is what you desire for your future, you can start your journey today by exploring combined masters and teaching credential programs online!

