If you’re interested in a career that allows you to travel high in the sky while managing the responsibilities of operating an aircraft, then you may be wondering how to become a pilot.

While there are a number of required steps to becoming a professional pilot, it is possible to obtain the appropriate qualifications in less time than you may think.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Becoming a pilot requires you to meet a number of different milestones throughout your pilot training programs, and you’ll continue to fulfill certain needs throughout your professional career.
How to Become a Pilot

Becoming a pilot is a process that requires hard work and dedication as you navigate medical examinations, flight school training, and rigorous testing.
If you’re interested in becoming a pilot, here are some of the steps required to earn your private pilot certification:
- Complete an introductory training flight. This provides you with a chance to take a good look at the work required as a pilot, get the perspective of being in an aircraft as an operator, get some initial flight experience, and get a sense of what it is like to be in charge of the controls.
- Complete your FAA medical certification. This is a medical clearance that is required in order to perform a solo flight, which is a requirement to graduate from flight school. FAA stands for the Federal Aviation Administration.
- Apply for your student pilot certification. This is another requirement needed to perform your solo flight during your aviation training program.
- Complete your flight training lessons. Your training can take you through different milestones, including the levels needed to become a private pilot, commercial pilot, and flight instructor. You can also get some flight experience and log your flight hours required for certification to become an airline pilot.
- Pass the FAA private pilot test and airmen knowledge test. These tests measure your knowledge of various aviation topics and culminate in the final step, which is a practical exam.
- Pass the practical examination. This oral and flight-based test is focused on evaluating your ability to act in accordance with the Airmen Certification Standards. It ensures that all flight safety measures are followed, you’re able to demonstrate a range of responsibilities that will be required of you in the operation of an aircraft.
Once you have completed these steps and have earned your private pilot license, you may go on to earn your commercial pilot certification and the airline transport pilot (ATP) certification.
Each certification requires the completion of the respective pilot knowledge test and an oral and practical examination, similar to those required as part of the private pilot licensing process. Each certification also requires the completion of a specified number of flight hours along with any appropriate flight ratings.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Notably, you are required to hold a private pilot license in order to qualify for a commercial pilot license, and you need to hold a commercial certification to qualify for the ATP certification. Other licenses you may choose to pursue could include your certified flight instructor certificate.
Pilot Certifications and Ratings

There are a number of different pilot certifications and pilot ratings that you may achieve throughout your aviation training and career.
Each pilot certification permits you to operate an aircraft of a certain size or type within specific parameters, such as whether you can fly with passengers on board. Pilot ratings, on the other hand, are add-ons to the various pilot certifications and can provide you with more flexibility in your certification.
Pilot Certifications
There are various pilot certifications that you may achieve throughout your career. Some of the certifications are mandatory, while others are optional.
- Student Pilot Certificate. A student pilot certificate is one of the certifications that you’re required to obtain in order to become a professionally licensed pilot. This certification is needed in order for you to complete your solo flight towards the end of flight school.
- Sport Pilot Certificate. In order to obtain a sport pilot certification, you’ll need to hold an active student pilot certificate. While you have more flexibility and freedom with this certification, there are still a number of limitations in terms of when you can fly, where you can fly, and what you can fly.
- Private Pilot Certificate. Earning your private pilot certificate allows you to fly most single-engine aircraft. At this level, though, you’re not allowed to earn money from flights. You’ll need to have completed your student pilot certificate in order to gain your private pilot certificate.
- Commercial Pilot Certificate. Commercial pilots can fly professionally and earn income from their flight time. Income-related flights are often limited to things like cargo flights, crop dusting, and aerial photography. A commercial airline pilot can receive permissions to transport passengers as well.
- Certified Flight Instructor Certificate. With a certified flight instructor certification, you may have the opportunity to provide instruction to aspiring pilots.
- Airline Transport Pilot Certificate. This certification allows you to fly passenger aircraft. Most pilots with this certification work for airlines. In order to achieve this certification and become a commercial pilot, you need to hold an active commercial pilot certificate.
In order to achieve each certification, you may be required to meet a specific set of criteria, including a designated number of flight hours and the completion of medical examinations, knowledge exams, and practical exams.
Pilot Ratings

Pilot ratings are features that can be added on to your certificates to provide you with additional allowances.
- Instrument Rating. Earning your instrument rating means that you’ve demonstrated your ability to follow instrument flight rules during flight. Having this rating will allow you to fly in conditions with poor visibility and cloud coverage.
- Multi-Engine Rating. Earning your multi-engine rating means that you’re able to operate aircraft with more than one engine.
- Seaplane Rating. Earning your seaplane rating allows you to operate seaplanes or floatplanes.
- Helicopter Rating. Earning your helicopter rating means that you are able to operate helicopters.
In most cases, you are required to at least hold your private pilot certificate in order to achieve the various pilot ratings available.
3 Things You Can Do as a Pilot

As a pilot, there are a number of different roles that you may be qualified to fulfill, such as the positions of an airline pilot, commercial pilot, and flight engineer.
1. Airline Pilots
Airline pilots are in charge of operating aircraft that transport passengers and cargo on a regular flight schedule. Part of these responsibilities could include overseeing flight crews and acting in the capacity of a pilot or co-pilot. Most airline pilots work for airlines.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Being a pilot can also involve monitoring aircraft balance, weight, fuel supply, engine functioning, and environmental conditions.
2. Commercial Pilots

A commercial airline pilot is responsible for the operation of an aircraft in regards to activities like aerial touring, private corporate flights, chartered flights, or aerial applications.
Once you become a commercial pilot, your additional responsibilities can include preparing flight plans, scheduling aircraft maintenance, and loading luggage.
3. Flight Engineer
Flight engineers can be in charge of monitoring and controlling instruments and operations during a flight. In some cases, flight engineers act as a third pilot during flights. This is a function particularly required on older model planes that do not have more modern, automated systems.
Aviation Careers and Salaries
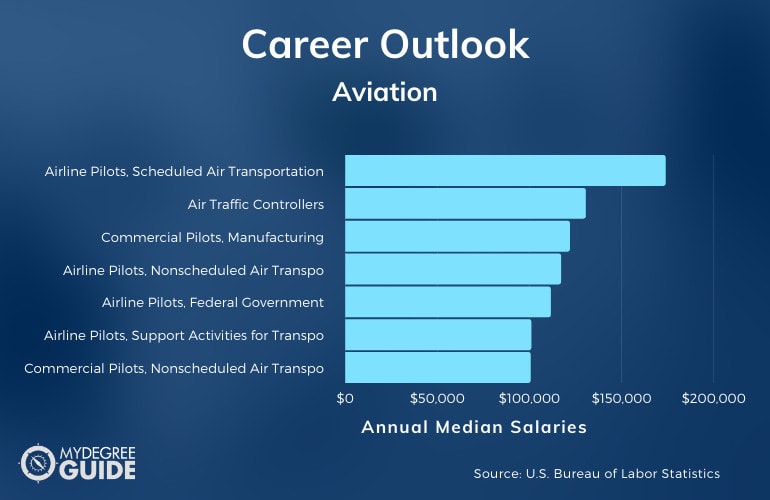
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there are a number of roles that pilots can pursue.
| Careers | Annual Median Salaries |
| Airline Pilots, Scheduled Air Transportation | $173,780 |
| Air Traffic Controllers | $130,420 |
| Commercial Pilots, Manufacturing | $121,830 |
| Airline Pilots, Nonscheduled Air Transportation | $117,030 |
| Airline Pilots, Federal Government | $111,460 |
| Airline Pilots, Support Activities for Transportation | $100,910 |
| Commercial Pilots, Nonscheduled Air Transportation | $100,530 |
| Commercial Pilots, Support Activities for Air Transportation | $85,080 |
| Commercial Pilots, Ambulance Services | $83,210 |
| Commercial Pilots, Private Technical and Trade Schools | $81,980 |
The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects 9% job growth for commercial pilots and 3% job growth for airline pilots, copilots, and flight engineers over the next ten years.
How to Choose a Flight School

When comparing the different pilot training programs available through various flight schools, there are a number of considerations to take into account, including:
- The level of flight experience they can offer
- The standard of instruction
- The approval status of the schools programming
- The relationship between the school and the FAA
- The type and number of aircraft available for training
- Graduation rates
- The hire or employment rates of graduates
Other considerations you may want to take into account are the diversity within the school or program, the overall costs and program fees, and the cost of living in the area of the school.
Accreditation

Regional accreditation is a status that is attributed to schools that meet a specific level of academic quality.
Attending a flight school that has been granted regional accreditation is an important consideration. This status can impact your ability to obtain employment, given that some employers place higher regard on accredited programming.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
The accreditation status of the program you attend may also impact your ability to obtain the required certifications needed to work as a professional pilot. For more information on the accreditation status of the school you’re interested in attending, you can visit the US Department of Education’s website.
Is Financial Aid Available?

Your journey to become an airline pilot may come with costs, but there are financial aid opportunities that may assist you if you qualify. Financial aid can come in the form of:
- Federal and state aid. The federal and state governments have grants and loans available to qualifying students.
- Scholarships. Scholarships are made available by both public and private organizations. In many cases, scholarships are directed toward specific areas of study
For more information on financial aid opportunities that may be available to you, you can visit the US Department of Education’s website and fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
What Does a Pilot Do?

While the responsibilities of pilots can vary depending on the specific role or position that they fulfill, common job responsibilities include the navigation of an aircraft. This could include small planes, private planes, helicopters, cargo planes, or passenger aircraft.
As part of their duties, pilots perform aircraft inspections before and after a flight, plan flight routes, and respond to changes in the environment or flight plan as needed. They also monitor the fuel supply and engine functioning, control aircraft balance and weight data, and oversee the safety of any crew members or passengers.
Do You Need a College Degree to Be a Pilot?
Whether or not a college degree is required to become a pilot depends on the type of work you’re looking to pursue and the type of employer you’re hoping to work for.
Regional airlines are less likely to require you to hold a degree in order to qualify for vacancies. Major airlines, on the other hand, often require their pilots to hold a bachelors degree.

Notably, most major airlines that require their pilots to hold a degree do not specify that the degree needs to be in aviation. Instead, it is generally accepted that your education can be in any area of study.
What Are the Requirements to Be a Pilot?
There are a number of certifications and ratings required to become a certified and licensed pilot. To earn your private pilot certificate, which allows you to fly solo, you have to be proficient in English and at least 17 years old.
Here are some of the steps to acquiring your private pilot certificate:
- FAA medical certification
- Student pilot certification
- Flight training lessons
- FAA private pilot test and airmen knowledge test
- Private pilot practical examination
Once you’ve earned your private pilot certification, you can then go on to become a commercial pilot by earning your commercial pilot certification followed by your airline transport pilot (ATP) certification. To become an airline pilot, you are also required to hold instrument and multi-engine ratings.
How Hard Is It to Become a Pilot?

Becoming a pilot takes dedication and perseverance to complete all the required elements, from your introductory flight and medical clearance to flight school and your final examinations.
Whether or not you find the process difficult may depend on your confidence in the cockpit as well as your ability to understand the technical aspects of flight operation.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
As part of your flight studies, you’ll likely take courses that cover topics like principles of flight, navigation and flight planning, federal aviation regulations, and flight maneuvers. You’ll also learn how to understand weather forecast information.
Where Do Pilots Work?

Where a pilot works depends on the type of job they pursue and the employer or client that they work for.
In terms of the aviation industry, pilots may work in scheduled air transport, the federal government, nonscheduled air transport, agriculture, ambulance services, manufacturing, or education (Bureau of Labor Statistics).
Additionally, depending on the type of pilot you’re interested in becoming, you may work regionally, nationally, or internationally.
How Much Do Pilots Make?

The amount that a pilot can make can vary depending on several factors, including their flight experience, employer, location of employment, and pilot ratings.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, pilots, copilots, and flight engineers make a median salary of $160,970 per year. A commercial airline pilot makes a median of $93,300. Exact earnings can vary greatly across different positions in the aviation industry.
For instance, the median salary for pilots who work in scheduled air transportation is $173,780, while the median for a commercial airline pilot who works in nonscheduled air transportation is $100,530 (Bureau of Labor Statistics).
How Much Does It Cost to Become a Pilot?

The cost to become a pilot depends on a number of factors, including the type of aircraft, the type of certifications, and the number of flight hours required.
The tuition and the total cost of flight training can vary, but you can expect to pay between $11,000 to $14,000 when pursuing your private pilot license. Earning your commercial certificate may cost an additional $3,000 to $5,000.
If you’re interested in working for a major airline, completing a college degree and an airline transport pilot license can also increase the cost of becoming a pilot. There are some pilot degree programs that include flight training and certification tracks.
Should I Become a Pilot?

How do you know if becoming a pilot is the right path for you? You might want to consider whether you enjoy flying in planes, whether you like to travel, and whether you’re comfortable being in control of an aircraft. Oftentimes, pilots have nontraditional work schedules. They may be flying on evenings, weekends, and holidays.
Pilots also need to pass the FAA medical requirements in order to complete solo flights. You may want to look up the medical requirements ahead of time to see if there are any health obstacles for you.
How Long Does It Take to Become a Pilot?
Aviation students can generally become pilots in 3 to 4 years. The length of time required to become a pilot will vary depending on the type of certification you’re interested in pursuing. How long it takes will also depend on how quickly you can get through flight school and complete your required flight hours.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
To become a commercial pilot, you’re required to complete 150 to 250 flight hours. This is a prerequisite for the airline transport pilot certification, which requires you to log at least 1500 flight hours. Earning a college degree can impact your timeframe as well, though a number of aviation programs include flight training and certification tracks.
What’s the Difference Between a Part 61 vs. 141 Flight Training Program?

Both Part 61 and Part 141 training programs are based on the Federal Aviation Regulations and focus on teaching FAA practical test standards. There are important differences between the two training options, though.
- Part 61: Part 61 focuses on the regulations for pilot certification. It is a less structured training program than Part 141 programs.
- Part 141: Part 141 focuses on regulations for flight training schools. Curriculum for Part 141 programs require FAA approval.
It may be possible to complete flight training in Part 141 programs faster than Part 61 programs.
Is Becoming a Pilot Worth It?

Yes, becoming a pilot is worth it for many professionals. Many pilots find flying to be a rewarding career. It can be an exciting path for those who enjoy travel and want to break free of the traditional office environment.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the profession of piloting is predicted to experience growth over the next ten years. Commercial pilots are expected to experience 9% job growth, and employment for pilots, copilots, and flight engineers is expected to grow 3%, which makes being a pilot worth it for many people who enter this career path.
Earning Your Pilot Degree Online

If you’re interested in getting behind the controls of a cockpit, navigating aircraft in the sky, preparing flight plans, and traveling, then becoming a pilot could be a rewarding career path.
You can obtain your pilot certifications through a flight school, or you can earn an aviation college degree that includes flight training. Either option can help you take to the skies.
There are even accredited schools that offer online aviation degree programs. You may be allowed to complete your coursework online while completing your flight training at an approved facility near you. As an alternative, some students choose to enter an online aviation management degree program, which combines the study of aviation and business management.
By exploring flight schools and aviation degrees alike, you can discover which path or program best aligns with your interests and career goals.

