Are you wondering how to become a therapist without a psychology degree? You be may asking this question if you’ve completed a portion of your education, such as an undergraduate degree, and are looking to transition into a new career as a therapist.

Therapists are an important resource for many individuals, couples, and families because they help them navigate stressful, emotional, or traumatic life events and circumstances.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Careers in therapy tend to offer higher than average salaries and positive job growth when compared to many other occupations. It’s even possible to consider becoming a therapist later in life, as the field can be a good fit for older workers.
How to Become a Therapist without a Psychology Degree

The path to becoming a therapist without a psychology degree includes several steps. The specific steps may vary depending on the state you’re interested in practicing in and the type of therapist you’re interested in becoming.
Certain therapist roles, such as marriage and family therapists, educational or school therapists, and organizational therapists, may only require you to hold a master’s degree. Other positions, such as clinical psychologists and counseling psychologists, require a PhD or PsyD.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
The difference in educational requirements lies in the type of work you’re looking to do and whether you want to work as an unlicensed or licensed therapist.
Here are common steps that need to be taken to become a therapist:
- Complete a bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution. While it may be fitting to complete your undergraduate degree in psychology, it is not necessary in order to become a therapist.
- Enroll in a psychology graduate program. It’s at the level of masters and doctoral studies where you need to complete your education in psychology or a similar field in order to become a therapist. The type of graduate degree you need depends on your overall career goals and state licensure requirements.
- Gain work experience. To become licensed as a therapist, you will likely need to complete a specific number of supervised clinical work hours. The exact requirement will vary from one state to the next.
- Take the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology. The final step to becoming a licensed therapist is to complete and pass the EPPP.
Though you may wonder what masters degree you can get with a bachelors in psychology, you may want to consider that there are many master’s and doctorate programs in psychology that do not require students to have a bachelor’s in psychology. Some of these universities may require you to take bridge courses or certificates to introduce you to key psychology principles though.
What Qualifications Do You Need to Be a Therapist?

Many find that becoming a therapist is a rewarding career goal, but there are a number of skills and qualifications needed to enter and be successful in the profession.
A couple of qualifications that may be required for you to become a therapist are:
- Master’s or doctoral degree in psychology: The level of education you will need depends on the type of therapy work you’re interested in pursuing.
- Licensure: Depending on your career goals, you may need to become licensed in order to practice in your state of choice.
There are many skills and traits that can be useful as a therapist as well, including:
- Empathy
- Communication skills
- Critical thinking skills
- Ability to set boundaries
All of these things can help you become an effective therapist that is ready to help others.
Common Pathways to Becoming a Therapist
A bachelor’s degree, even one unrelated to psychology, is not enough to become a therapist, but it is the first step in the process.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
After earning your bachelor’s degree, you’ll need to pursue additional education in the form of graduate studies. This may include various master’s and doctoral level programs, such as a master’s in counseling, social work, or marriage and family therapy or a PhD in psychology.
Master’s in Counseling

Earning a master’s in counseling can help you become a therapist in several different professional areas, ranging from mental health to education.
While pursuing your master’s in counseling, you may have the option to choose between different specialties. Some options may include clinical mental health counseling, school counseling, substance abuse counseling, and applied behavior analysis.
Common topics for this degree are human growth and development, counseling theories, treatment of psychopathology, principles of psychotherapy, and group therapy practices.
Master of Social Work

Earning a Master of Social Work may not only allow you to break into the field of therapy, but it may also connect you with work in advocacy, policy, and child welfare.
Graduate degree programs in social work commonly require studies in the foundations of social work practice, social environment, human rights and social justice, and social policy analysis. Other common topics of study are psychopathology and clinical social work practices.
As part of your degree, you may choose to focus on child and family, addictions, healthcare, trauma-informed practice, or the military.
Master’s in Marriage and Family Therapy

Earning a master’s in marriage and family therapy can help you play an important part in helping individuals, couples, and families cope with stress, conflict, and difficult life circumstances.
Marriage and family therapy programs typically require courses in couples and family counseling, human sexuality, and crisis and trauma response. Child and adolescent counseling practices and substance abuse are common topics of study as well.
PhD in Psychology or Doctor of Psychology (PsyD)

Earning a PhD in psychology or a Doctor of Psychology (PsyD) can help you become a licensed therapist or psychologist in most states.
These programs typically require intensive coursework in areas such as cognitive behavioral therapy, developmental psychopathy and treatment, and organizational psychology.
Marriage and family psychology, biological bases for behavior, ethical issues in psychology, and approaches to psychotherapy are common topics of study as well. In order to work as a clinical psychologist a license and usually a doctorate-level education are required.
Masters in Psychology Specialty Areas

While pursuing your master’s in psychology, you may have the option to choose from a number of specialty areas to help craft your education into a more concentrated and focused study plan.
Potential specialty areas include:
- Applied behavioral analysis: This specialty is focused on understanding developmental disabilities to help individuals and families manage various behaviors and improve the lives of those with different disabilities.
- Applied psychology: This focus of study is designed to provide an in-depth understanding of principles, methods, and theories in the field of psychology from a research and practical application perspective.
- Educational psychology: This specialty is designed to provide an understanding of different educational abilities and the psychological factors related to those varying abilities.
- Health psychology: This specialty focuses on understanding health through biological, social, and psychological lenses.
Available specialty options may vary from one school to the next.
3 Things You Can Do with a Therapy Degree

There are a number of different career paths available for you to pursue with a therap degree. You might pursue a job as a marriage and family therapist, correctional treatment specialist, or substance abuse counselor, to name a few.
1. Marriage and Family Therapist
Marriage and family therapists help individuals, couples, and families work through complex issues. This may include assessing communication issues and developing strategies to improve familial communication.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Marriage and family therapists may also help partners work through stressful life events or help patients understand and manage their mental health issues.
2. Correctional Treatment Specialist
Correctional treatment specialists work closely with forensic populations. These include young offenders, adult offenders, inmates, and those experiencing mental health and substance abuse issues.
In this role, you may support individuals and groups in the rehabilitation process. This might include the assessment of offenders in order to advocate for or against their readiness for parole or release. In some cases, correctional treatment specialists provide counseling support to the families of offenders.
3. Substance Abuse, Behavioral Disorder, and Mental Health Counselors

Substance abuse, behavioral disorder, and mental health counselors help individuals across a range of age groups cope with and manage their specific circumstances.
Their work often includes performing assessments of mental health, substance abuse, or behavioral issues. After assessments are complete, they provide recommendations for managing those issues and potential treatment options.
Many counselors in this field also work closely with families to help them understand the life experiences of family members dealing with these types of health issues.
Counseling & Therapy Careers
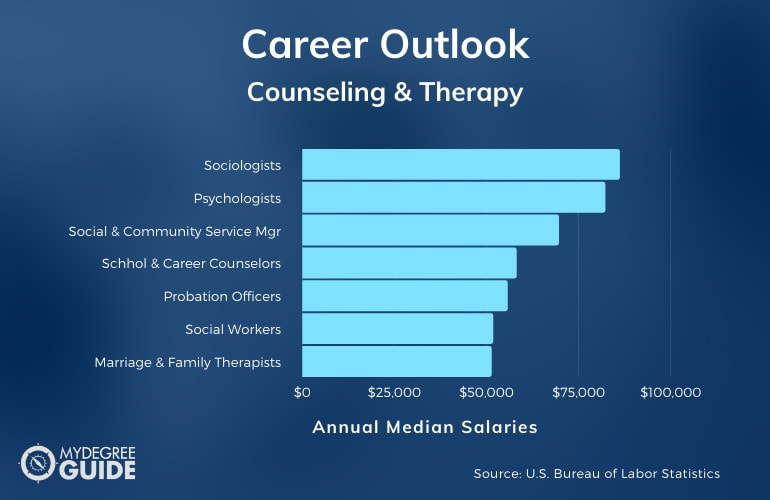
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, there are a number of counseling and therapy careers that may be available to you with a therapy degree.
| Careers | Annual Median Salaries |
| Sociologists | $86,110 |
| Psychologists | $82,180 |
| Social and Community Service Managers | $69,600 |
| School and Career Counselors and Advisors | $58,120 |
| Probation Officers and Correctional Treatment Specialists | $55,690 |
| Social Workers | $51,760 |
| Marriage and Family Therapists | $51,340 |
| Health Education Specialists and Community Health Workers | $48,140 |
| Substance Abuse, Behavioral Disorder, and Mental Health Counselors | $47,660 |
| Rehabilitation Counselors | $37,530 |
These are just some of the jobs you can pursue with a therapy degree. You can pursue careers in a number of different industries, including education, nonprofit, government agencies, hospitals, correctional centers, and private clinics.
Some of the jobs listed above may require additional licensure, education, or work experience to obtain.
Internship Opportunities

For many states, becoming a licensed therapist requires you to complete a specific number of clinical placement hours in order to become eligible for licensure. Internships, even at a master’s level, can be an important way of gaining relevant work experience in the field of psychology and therapy.
Some places that you may find rewarding and valuable internship opportunities include:
- On-campus counseling centers
- Hospitals and health clinics
- Mental health facilities
- Schools and other educational settings
- Correctional facilities
- Nursing homes
In some cases, you may have the opportunity to gain experience through an internship at a private practice or private counseling office. Connecting with an academic advisor for support and direction can help you find the right internship positions for your career goals.
Accreditation

Regional accreditation is a status that verifies the academic quality of various educational programs.
Attending an accredited therapy graduate program is an important consideration because it can impact your ability to register for various professional licensing bodies. It can also influence your ability to enroll in future academic programs.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
The accreditation status of the program you attend may also impact the hiring decisions of potential employers. For more information on regional accreditation, you can visit the Council for Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA).
Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs (CACREP)
The Council for Accreditation of Counseling and Related Educational Programs, or CACREP, is the programmatic accreditation for counseling and therapy. CACREP accredits graduate-level programs, including masters and doctoral programming.
Similar to regional accreditation, CACREP ensures a certain level of academic quality, but this accrediting body is specifically focused on programs in the field of counseling. Attending a CACREP accredited institution and program can help you ensure that the counseling education you’re receiving is of high quality.
Counseling and Therapy Licensure and Certifications

The process of becoming a licensed counseling and therapy professional may vary from one state to the next, but common steps in the process include:
- Obtain a PhD in psychology or Doctor of Psychology (PsyD) from an APA-accredited institution.
- Complete supervised work hours. While the specific number of hours can vary, the average number of hours required for licensure is 3000.
- Pass the Examination for Professional Practice in Psychology (EPPP)
In some cases, you may also be required to take a jurisprudence examination after successfully passing the EPPP.
What Does a Therapist Do?

The roles and responsibilities of a therapist can vary depending on the type of work they engage in and the types of individuals or groups they support.
In many cases, therapists work with individuals or groups of people to provide support through emotional, stressful, or traumatic life events. Therapists may also evaluate or assess individuals. They may work with children who have experienced abuse or have behavioral issues, adults in correctional institutions, or people needing mental health support.
Can You Become a Therapist Without a Psychology Degree?

How to become a therapist without a degree in psychology can be a common question for those who are interested in becoming a psychologist but don’t have bachelor’s degrees in psychology.
It is possible to become a therapist without having an undergraduate degree in psychology. You may be able to secure a position as a therapist at the organizational or educational level with a master’s degree in psychology or a related field. To act as a licensed psychologist or therapist, a PhD or PsyD may be required.
Where Do Therapists Work?
Therapists work in a variety of industries and environments. Some examples include correctional centers, educational institutions, hospitals, mental health centers, senior living facilities, individual or family services, child welfare, and nonprofits. It’s also common for therapists to be self-employed in private practices.
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
Pay can vary greatly depending on the type of therapy services you provide. For example, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, psychologists working for government agencies earn a median annual salary of $100,360. Those working in school systems, though, earn a median annual salary of $77,560.
How Much Do Therapists Make?
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, careers in therapy tend to earn more per year on average than many other occupations. Some of the highest-paid psychologists earn median annual salaries of $105,780. Industrial-organizational psychologists earn median annual salaries of $92,880.
Some positions, such as marriage and family therapists ($51,340) and mental health counselors ($47,660) earn less on average per year than the top-paying psychologist roles. They still have higher average earnings than other community and social service occupations though.
How Do You Become a Therapist without a Degree?

There are many types of therapist roles available in the workplace, some requiring a degree and others not. Certain positions, including mental health counselors, psychologists, and marriage and family therapists, require at least some education in psychology or a related field.
Other positions can be entered into without holding a degree. These may include:
- Peer support counselors
- Career counselors
- Substance abuse counselors
- Life skills counselors
- Youth workers
- Community outreach workers
It’s worth noting that specific entry-level requirements can vary from one employer to the next.
What Degree Do You Need to Be a Therapist?

To become a psychologist or licensed therapist, it is common to need a graduate degree in psychology. The specific requirements vary from one state to the next, but it is generally accepted that a doctorate in psychology is required in order to qualify for licensure.
In some cases, you may be eligible for positions, such as an organizational psychologist or school therapist, without a PhD or PsyD. For these positions, a master’s degree in psychology may suffice.
How Many Years of College to Be a Therapist?

Pursuing the path of a licensed therapist commonly requires 4 to 6 years of graduate-level education, though the number of years required to become a therapist varies from state to state. Prior to enrolling in a graduate-level program, you will likely need to complete an undergraduate degree, which usually takes around 3 to 4 years.
After your undergraduate studies, you may decide to enroll in either a master’s program or a doctorate program. Master’s degrees generally take 2 years, while doctorate degrees can take around 4 years to complete.
Should I Become a Therapist?
When deciding on whether or not you should become a therapist, there are a number of questions you may want to ask yourself, including:
- Are you interested in working with individuals, families, and groups of people on a regular basis?
- Do you have the patience and empathy to listen to individuals and understand their perspectives and experiences?
- Are you interested in investing a number of years toward obtaining the necessary skills and knowledge to become a therapist?
- Do you have effective communication skills
If you answered yes to these questions, then becoming a therapist may be right for you. If you answered no, you may want to consider other options or work on some of the skills that are listed before becoming a therapist.
What’s the Difference between a Psychologist vs. Therapist?

Psychologists’ and therapists’ roles and responsibilities can overlap, and the key distinctions between the two depend on the field or industry that each position is being performed in.
Psychologists:
- Work is typically focused on counseling or research
- May be licensed or unlicensed
- Usually need a PhD
- Able to perform clinical counseling
Therapist:
- Work is generally centered around counseling
- May be licensed or unlicensed
- Education level could be a master’s or doctorate level
In some cases, the titles of psychologist and therapist may be used interchangeably.
What’s the Difference between a Counselor vs. Therapist?

The titles of counselor and therapist are also often used interchangeably. In many cases, the roles and responsibilities of these professions overlap, but some differences can exist.
Counselors:
- May provide services more short term than a therapist
- States may have specific counselor licensing requirements
Therapists:
- Services may be provided over a longer period of time
- States may have specific therapist licensing requirements
Additionally, therapists are commonly trained in the practice of psychotherapy, unlike counselors.
Getting Your Therapist Degree Online

There may be a number of ways for you to become a therapist without having a psychology degree.
Various education pathways, from a master’s in psychology to a master’s in marriage and family therapy, social work, or counseling, may be options. A PhD or PsyD can also help you become a therapist. Careers in the field of therapy are available across multiple areas, ranging from criminal justice and law to mental health and family services.
Plus, there are a number of universities that offer psychology degrees online. In fact, a growing number even offer dual masters and PhD programs in psychology online, allowing you to earn both degrees at the same time.
With higher than average annual salaries, pursuing the path to becoming a professional therapist may offer you a good return on your investment.

